Tonsils play a significant role in our immune system, acting as the body’s first line of defense against germs entering through the mouth and nose. However, they are not immune to problems themselves. Sometimes, tonsils need to be removed due to recurrent infections or other health concerns. This leads to the question: Can tonsils grow back after removal? In this article, we will explore tonsil health, the possibility of tonsil regrowth, and what you should know about keeping your throat healthy.
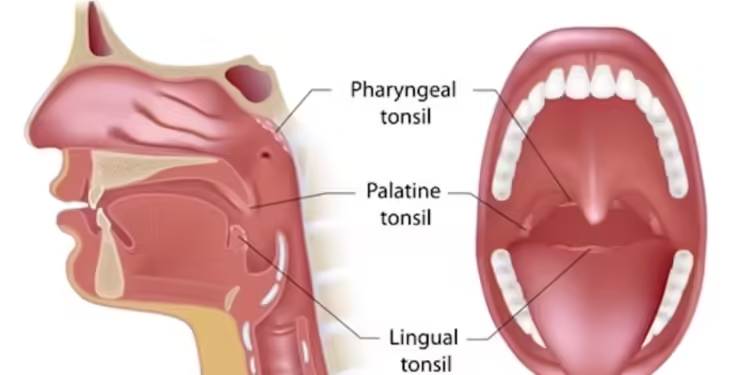
What Are Tonsils?
Tonsils are small, oval-shaped masses of tissue located on both sides of the back of your throat. These glands are part of the lymphatic system, which helps your body fight infections by trapping bacteria and viruses. Tonsils produce antibodies that target germs before they spread further into the body, making them crucial for immune defense, especially during childhood.
However, as you age, the role of the tonsils diminishes, and your body relies on other immune structures to fend off infections. This reduction in their immune function means that, while tonsils are essential for young children, they become less critical as we grow older. Despite this, tonsils can sometimes become problematic, leading to frequent infections or swelling that requires medical attention, including surgical removal.
Why Do People Get Their Tonsils Removed?
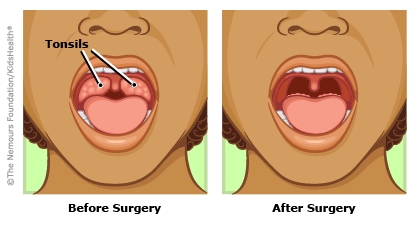
There are several reasons why people undergo a tonsillectomy, the surgical procedure to remove tonsils. This operation is relatively common, especially in children, but it can also be performed on adults. The most common reasons for tonsil removal include:
- Chronic Tonsillitis: Repeated episodes of tonsillitis, which involve inflammation of the tonsils due to infection, can lead to severe throat pain, fever, and difficulty swallowing. If tonsillitis occurs frequently, a doctor may recommend removing the tonsils to prevent future infections.
- Sleep Apnea: Enlarged tonsils can obstruct the airway, especially during sleep, causing sleep apnea. This condition leads to interrupted breathing and can cause a range of health issues, from poor sleep to heart problems. Tonsil removal can help alleviate these symptoms.
- Difficulty Swallowing or Breathing: Sometimes, enlarged tonsils can interfere with normal breathing or swallowing. In such cases, removing the tonsils may be necessary to improve quality of life.
- Tonsil Stones (Tonsilloliths): These are hard, calcified deposits that form in the crevices of the tonsils. They can cause discomfort, bad breath, and infections, and in severe cases, tonsil removal may be the best solution.
The decision to remove tonsils is typically made after a patient has experienced recurring symptoms that significantly impact their health and well-being.
Can Tonsils Grow Back After Removal?
One of the most common questions following a tonsillectomy is whether tonsils can grow back. In most cases, once the tonsils are removed, they do not fully regenerate. However, in some rare instances, small remnants of tonsil tissue may remain after surgery. This residual tissue can potentially grow over time, though it usually doesn’t cause the same level of problems as the original tonsils.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-517151357-5862589f3df78ce2c3d9eec9.jpg)
What Causes Tonsils to Grow Back?
Tonsil regrowth is rare, but it can happen if some tissue is left behind during the surgery. The remaining tissue may slowly enlarge, especially if it is exposed to frequent infections or irritation. Some factors that could contribute to tonsil regrowth include:
- Partial Removal: If a tonsillectomy is not fully complete, the remaining tonsil tissue has the potential to grow back. This is more common in surgeries where only part of the tonsil is removed, rather than a complete tonsillectomy.
- Childhood Tonsillectomy: Children who undergo tonsil removal may experience slight regrowth due to the body’s natural healing and tissue regeneration processes. However, the regrowth is usually minimal and doesn’t result in the same issues that led to the tonsillectomy.
- Repeated Infections: Chronic infections or inflammation can trigger the growth of any remaining tissue. However, this regrowth is often limited and unlikely to cause significant health problems.
What Should You Do If They Grow Back?
If you notice symptoms similar to those you experienced before your tonsillectomy, such as sore throat, difficulty swallowing, or frequent throat infections, it’s possible that your tonsils may have regrown. While tonsil regrowth is uncommon, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect it. They may recommend the following steps:
- Medical Examination: Your doctor will likely perform a physical examination to assess the situation and determine if regrowth has occurred.
- Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection is present, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to clear the infection.
- Further Surgery: In rare cases where regrown tonsil tissue causes persistent problems, a second tonsillectomy may be recommended to remove the remaining tissue.
Can You Prevent Tonsils from Growing Back?
There is no guaranteed way to prevent tonsils from regrowing, as the potential for regrowth depends on the completeness of the original surgery. However, you can take steps to reduce the risk of infections and inflammation, which may help minimize any issues with the remaining tonsil tissue:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep your throat moist and reduces irritation.
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing your teeth regularly and using mouthwash can help prevent bacterial infections in the throat.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can irritate the throat and increase the risk of infections, so avoiding tobacco products is crucial for throat health.
- Gargle with Salt Water: Gargling with warm salt water can soothe a sore throat and prevent infections.
Signs Your Tonsils Might Be Growing Back
If you’ve had your tonsils removed but start experiencing symptoms like a sore throat or difficulty swallowing again, you might wonder if your tonsils are growing back. Some common signs that could indicate tonsil regrowth include:
- Frequent Sore Throat: Persistent sore throats could be a sign of tonsil tissue regrowth or another throat infection.
- Difficulty Swallowing: If swallowing becomes painful or uncomfortable, it could signal the presence of regrown tonsil tissue.
- Tonsil Stones: The reappearance of tonsil stones may indicate the presence of leftover tonsil tissue.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: If your lymph nodes become swollen or tender, they may be related to inflammation in the throat or possibly to residual tonsil tissue.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice to determine the cause and the best course of action.
How to Keep Your Throat Healthy
Keeping your throat healthy is important, especially if you have a history of tonsil problems. Here are some tips to help maintain throat health:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids can help keep your throat moist and reduce the risk of irritation.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help boost your immune system and keep your throat healthy.
- Avoid Irritants: Avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke, pollution, and other irritants can help prevent throat problems.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently and avoid close contact with sick individuals to reduce the risk of infections.
- Manage Allergies: If you suffer from allergies, managing them properly can help prevent throat irritation and swelling.
When to See a Doctor
If you’ve had your tonsils removed but continue to experience throat problems, it’s important to know when to seek medical attention. You should see a doctor if you experience:
- Persistent Sore Throat: A sore throat that lasts more than a few days or worsens over time.
- Difficulty Breathing or Swallowing: If you find it difficult to breathe or swallow, this could be a sign of a serious problem.
- Frequent Infections: If you experience repeated throat infections, it may be time to consult a doctor.
- Fever and Fatigue: A high fever and fatigue may indicate an infection that requires medical treatment.
How Does Tonsil Removal Work?
A tonsillectomy is typically performed under general anesthesia and involves removing the tonsils either with a scalpel or newer techniques such as radiofrequency ablation or laser surgery. The procedure usually lasts about 30 to 45 minutes. Most people can go home the same day, although recovery can take up to two weeks. Pain management, rest, and following the doctor’s post-operative care instructions are critical for a smooth recovery.
What Happens if Tonsils Grow Back?
If tonsils regrow, they may cause some of the same issues that led to their initial removal, such as sore throats, infections, or difficulty swallowing. However, regrowth is usually limited and may not require additional surgery unless it leads to significant problems. If you experience recurring symptoms, your doctor may recommend further evaluation and treatment.
Symptoms of Tonsil Problems
Common symptoms of tonsil problems include:
- Sore Throat: This is one of the most common signs of tonsil problems.
- Bad Breath: Chronic tonsil infections or the presence of tonsil stones can cause persistent bad breath.
- Swollen Tonsils: Enlarged or inflamed tonsils may cause pain and discomfort.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Swollen tonsils can make it hard to swallow food or liquids.
- Ear Pain: Referred pain from inflamed tonsils can sometimes be felt in the ears.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Signs You Might Need Tonsil Surgery
If you’ve experienced frequent tonsil problems, you might be wondering whether surgery is the right option for you. Some signs that indicate you may need a tonsillectomy include:
- Frequent Infections: If you suffer from multiple episodes of tonsillitis each year, a tonsillectomy may be recommended to prevent further infections.
- Breathing Issues: Enlarged tonsils can obstruct the airway, leading to breathing difficulties or sleep apnea.
- Tonsil Stones: If tonsil stones are causing chronic discomfort or bad breath, removal of the tonsils may be a long-term solution.
It’s important to discuss your symptoms with a healthcare provider to determine whether tonsil surgery is necessary for you.
Final Words
Understanding whether tonsils can grow back after removal is important for those who have undergone or are considering a tonsillectomy. While regrowth is rare, it can happen if any tonsil tissue remains after surgery. Keeping your throat healthy through proper hygiene, hydration, and managing infections can help prevent issues related to tonsil regrowth. If you suspect your tonsils have grown back or are causing problems, consult with a healthcare provider for proper guidance.
By staying informed about tonsil health and taking the necessary precautions, you can maintain a healthy throat and avoid complications related to tonsil issues.